Getting Started Guides
- Home /
- Categories /
- Getting Started Guides
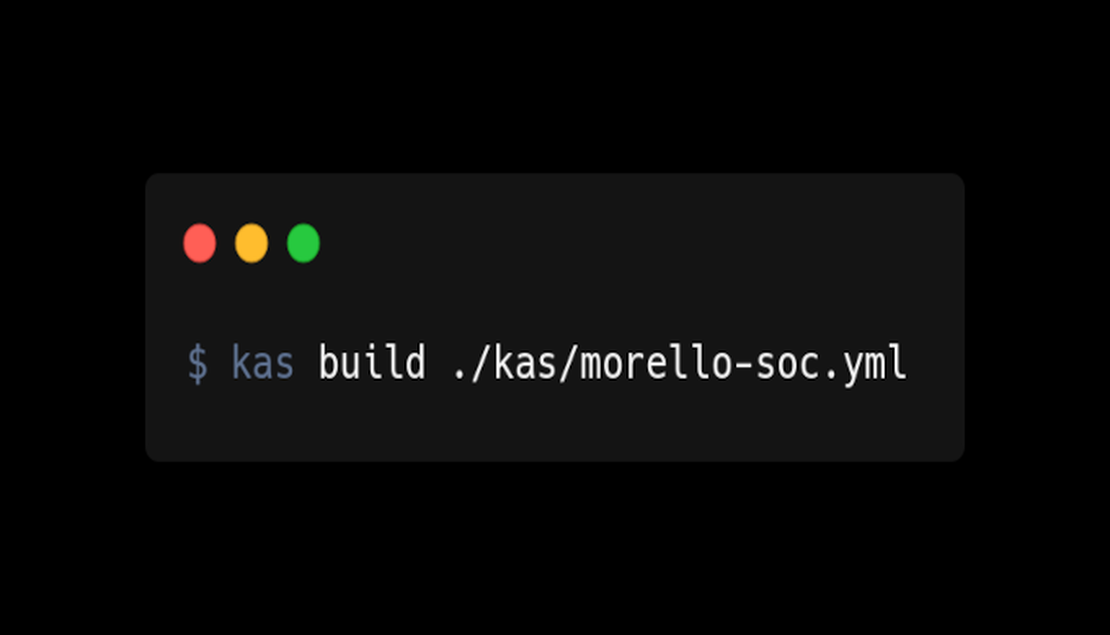
Getting Started with Morello and Yocto
The ‘Morello’ project was an experimental research architecture developed by ARM that implemented the CHERI instruction extensions. The hardware was based on Neoverse N1 core, which itself was based on the Armv8.2-A architecture specification, but it was constrained to ‘AArch64’ execution only. The memory tagging functionality (which is required to accommodate the capabilities) was managed by a custom memory controller and interconnect: tags were stored in the DDR ECC bit or in DRAM at the top of physical memory address space.
Read More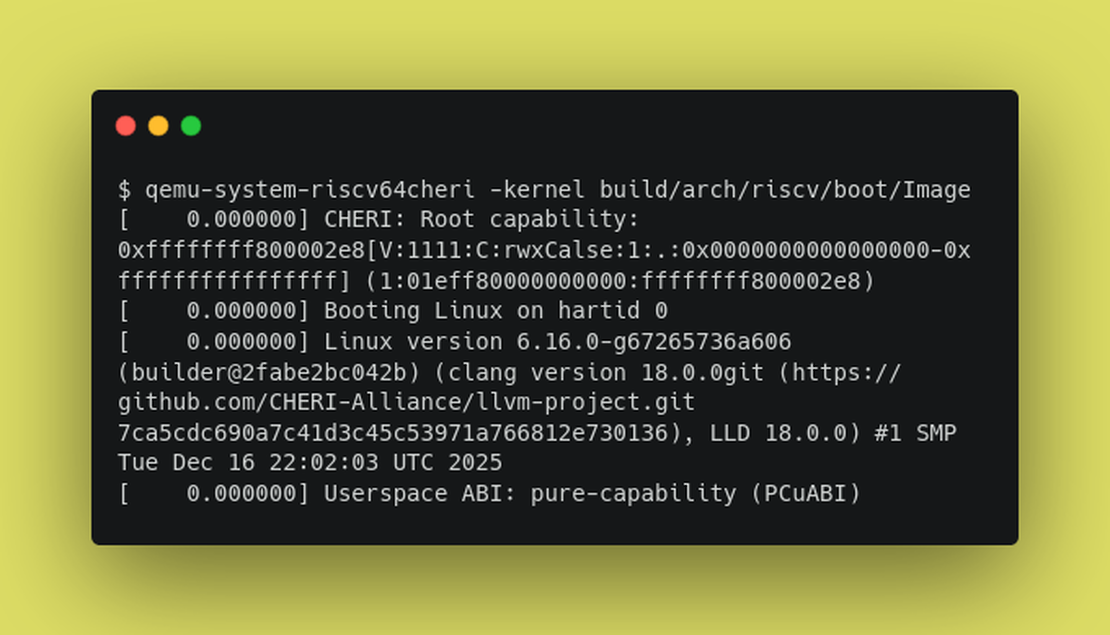
Getting started with CHERI Linux on RISC-V
In this post, we’ll walk through the steps required to build a CHERI-enabled Linux kernel for RISC-V and boot the said kernel using QEMU. Most of the effort to add support for CHERI targets is taking place within forks hosted by the CHERI Alliance. We’ll cover how to build the CHERI Alliance’s forks of LLVM, RISC-V OpenSBI firmware and Linux kernel, along with CHERI Alliance’s fork of QEMU which supports emulation of RISC-V CHERI architecture (the CHERI extensions to the RISC-V instruction set is formally known as RISC-V RVY architecture).
Read More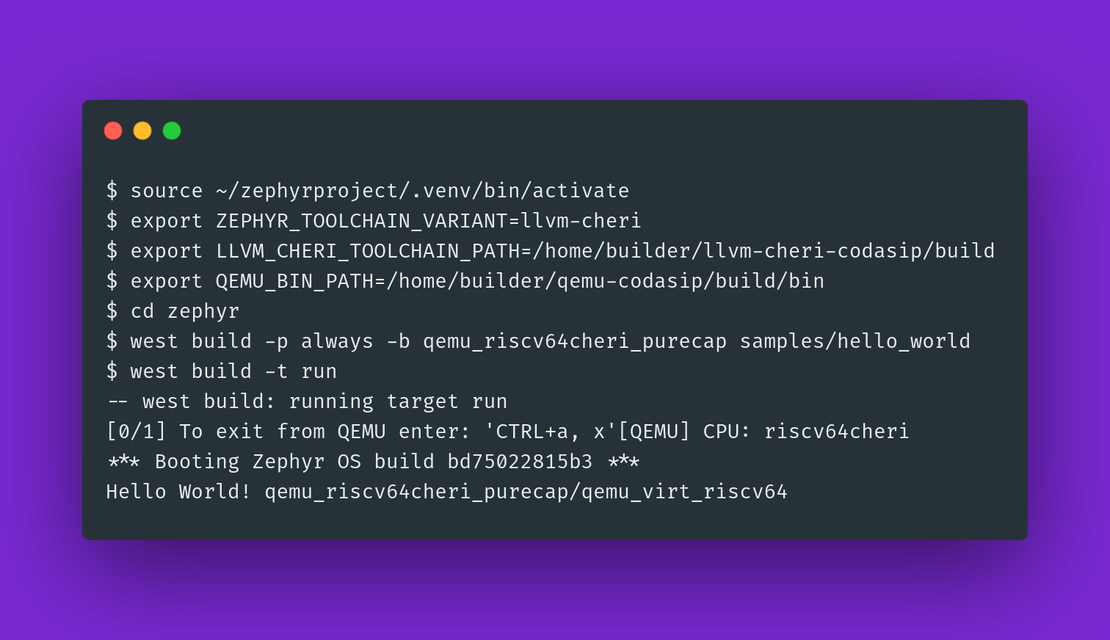
Getting Started with CHERI-Zephyr: Setup, Build, and Run
The University of Birmingham recently received funding to continue developing CHERI support in the Zephyr RTOS. This is part of a wider £21 million investment from UKRI to back the development of CHERI-enabled hardware and the surrounding software ecosystem.
Read More